The medical world has made tremendous progress in cancer screenings and prevention. It is important for everyone, men and women alike, to understand their risk factors for certain types of cancer, and to be tested appropriately. There are sometimes different screening methods for each type of cancer and risks and benefits associated with each. Here are a few common types of cancer screening for men and women and the pros and cons of each. Please note that this information is not meant to discourage cancer screenings, but simply to provide information and encourage each individual to do their own research and make educated choices.
Men
Prostate Cancer – PSA screening (Prostate-specific antigen), which is a blood test.
Pro – PSA screening is used for early detection of prostate cancer. Detecting prostate cancer early significantly improves survival rates. Treatment and patient recovery for prostate cancer is much more successful with early detection. The survival rate has increased dramatically since the invention of PSA screening.
Con – According to the Mayo Clinic, most prostate cancers are slow-growing, which can mean a few things. Sometimes this means the cancer will never spread or grow enough to be life-threatening. It can also mean that a PSA screening won’t detect it. On the other hand, PSA tests can also give a false-positive, which leads to unnecessary treatment and all of the corresponding side-effects.
Colon Cancer – colonoscopy
Pro – This is the most sensitive test available, and a biopsy can be done at the time of the exam if any abnormalities are detected. A large, long-term study conducted by the Harvard School of Public Health found that with regular colonoscopies, 40 percent of all colorectal cancers could be prevented.
Con – A colonoscopy still might miss small cancer or polyps. In addition, diet and medication changes may be necessary prior to the colonoscopy.
Testicular Cancer – self-exam
Pro – A self-exam is easy to perform and is effective at detecting abnormalities and catching any cancer early.
Con – It can be easy to mistake blood vessels and tissue for irregular bumps or growths, leading to unnecessary appointments or further, more invasive treatments. The best way to ensure an accurate self-exam is to perform one regularly so you are familiar with your own anatomy, so if anything out of the ordinary does appear you’ll notice it immediately.
Women
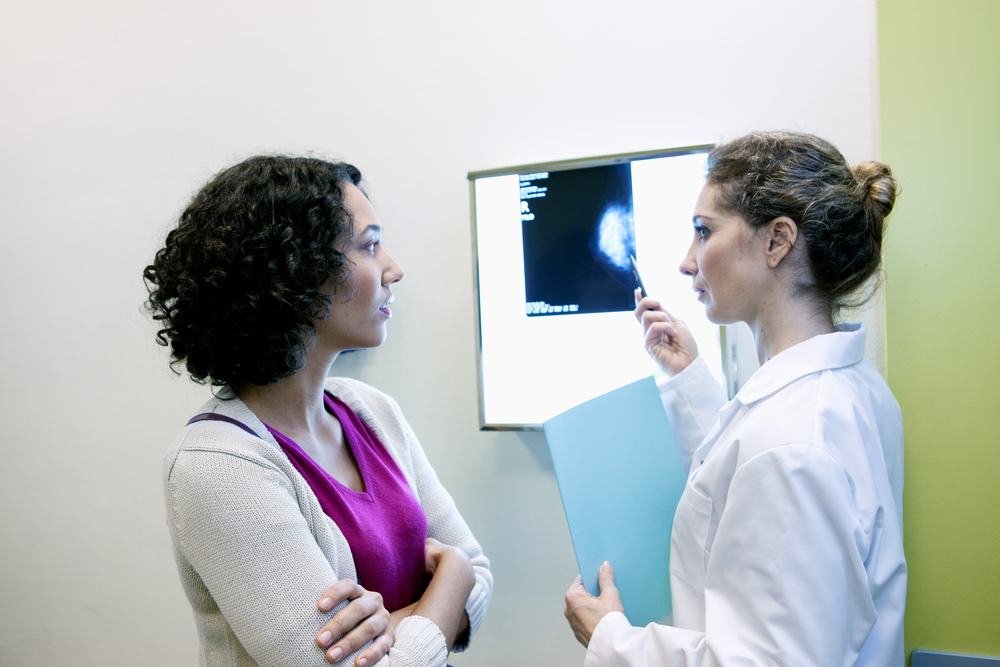
Breast Cancer – mammogram
Pros – Much research has found that mammograms do decrease the risk of dying from breast cancer. Several studies have shown a higher survival rate among women over the age of 50 who have regular mammograms. The American Cancer Society’s current recommendation is that women over the age of 40 should have a mammogram every year.
Con –False positives can occur, and many frequently detected cancers rarely develop into aggressive life-threatening cancers. As a result, many women are over-treated. In addition, a mammogram is ineffective for women with dense breasts or breast implants.
Cervical Cancer – Pap smear
Pro – Cervical screening can prevent three in four cervical cancers by early detection and intervention.
Con – This is one of the more invasive tests and is also known for bearing false positives, where cell changes evident on the test would clear up on their own and not lead to cancer. This can cause unnecessary anxiety and further tests and treatment.
Ovarian Cancer – ultrasound and blood test
Pro – When diagnosed early, ovarian cancer has a 90 to 95 percent survival rate.
Con – A transvaginal ultrasound can frequently produce abnormal results when no problems exist. A blood test measures for the CA-125 protein which is released by the ovaries and would be elevated if cancer was present, but that protein is also frequently released by other normal cells.



No Comment